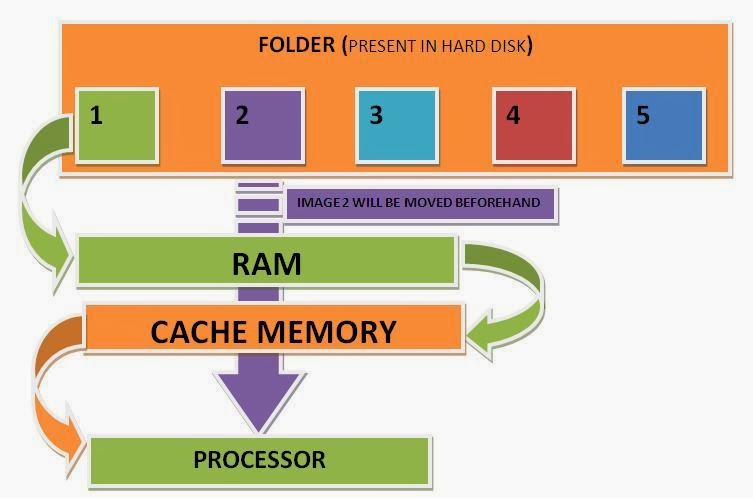
Cache (pronounced cash) memory is extremely fast memory that is built into a computer’s central processing unit (CPU),
or located next to it on a separate chip. The CPU uses cache memory to
store instructions that are repeatedly required to run programs,
improving overall system speed. The advantage of cache memory is that
the CPU does not have to use the motherboard’s
system bus for data transfer. Whenever data must be passed through the
system bus, the data transfer speed slows to the motherboard’s
capability. The CPU can process data much faster by avoiding the
bottleneck created by the system bus.
As
it happens, once most programs are open and running, they use very few
resources. When these resources are kept in cache, programs can operate
more quickly and efficiently. All else being equal, cache is so
effective in system performance that a computer running a fast CPU with
little cache can have lower benchmarks than a system running a somewhat
slower CPU with more cache. Cache built into the CPU itself is referred
to as Level 1 (L1) cache. Cache that resides on a separate chip next to the CPU is called Level 2 (L2) cache. Some CPUs have both L1 and L2 cache built-in and designate the separate cache chip as Level 3 (L3) cache.source of article .... http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-cache-memory.htm
No comments:
Post a Comment